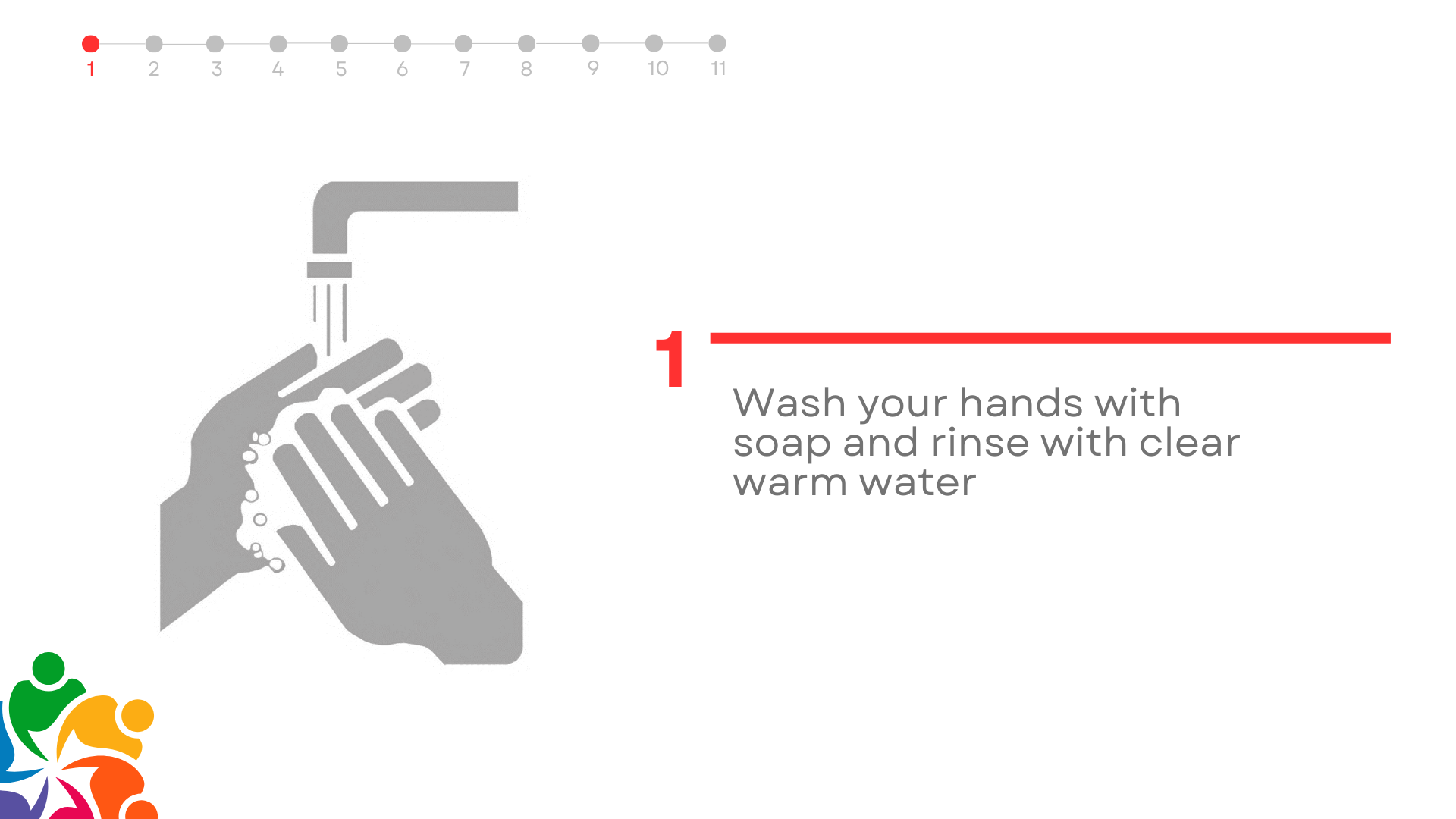
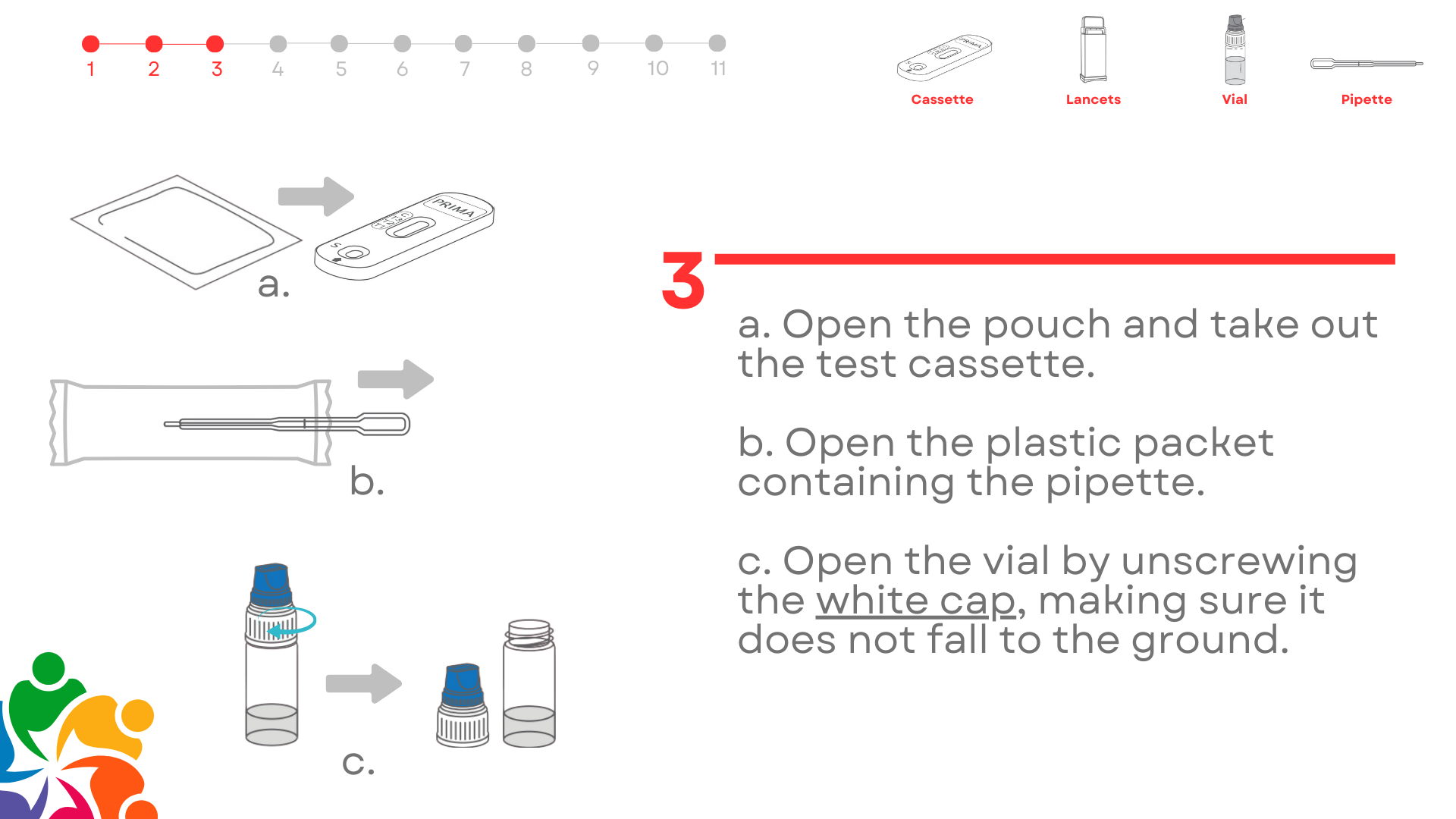
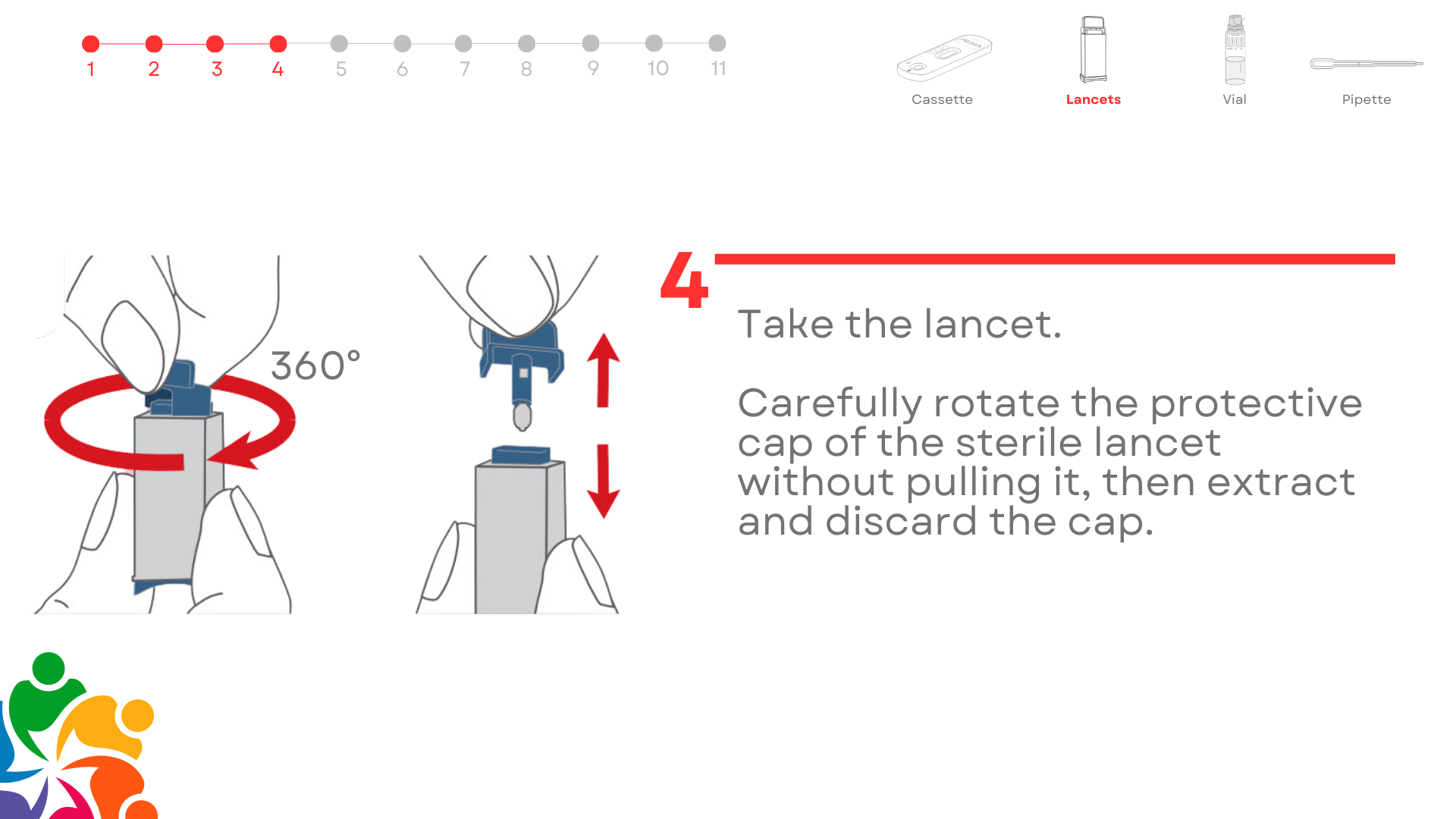
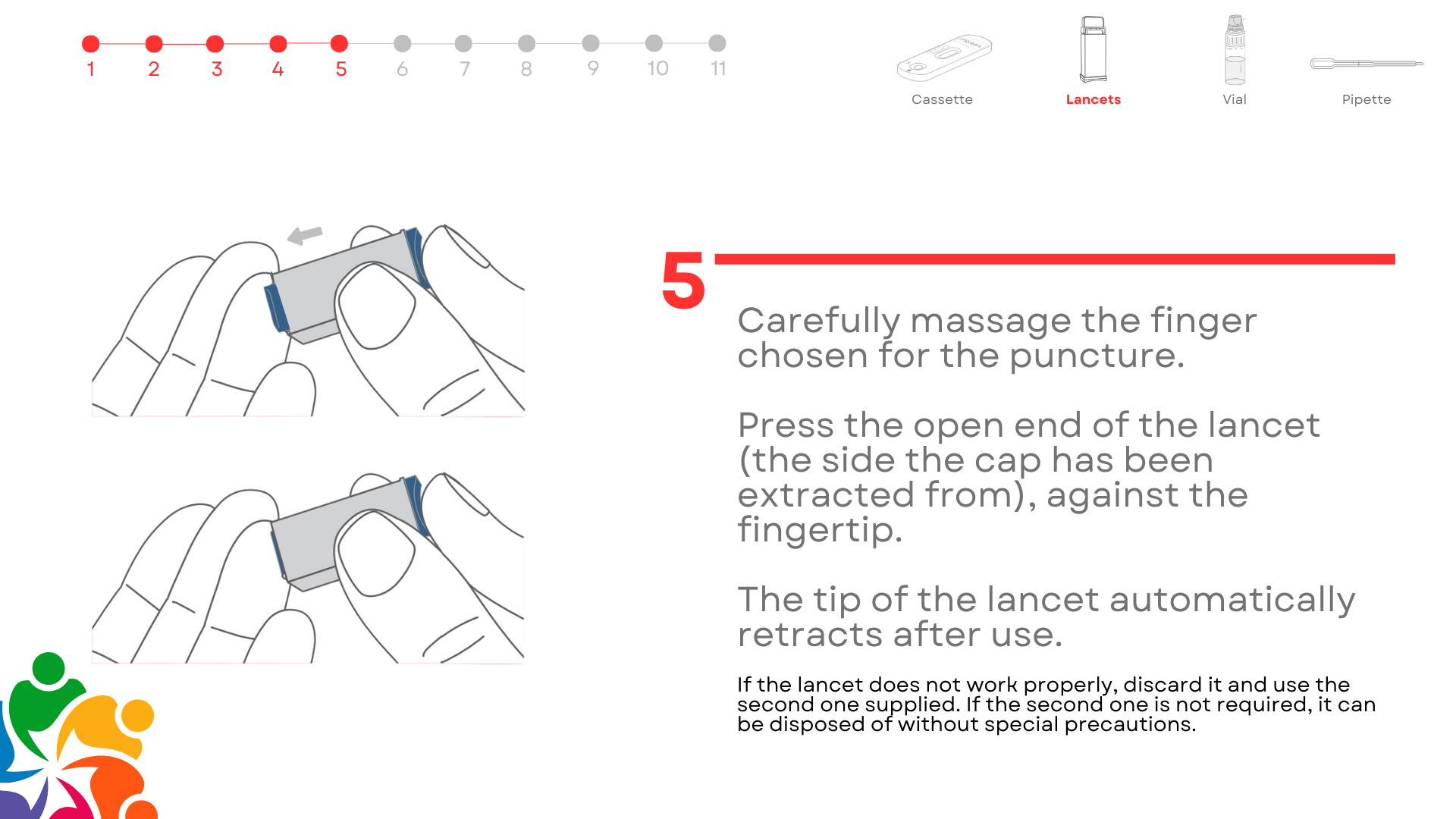
Test Overview
Symptoms
Since CRP can be linked to many conditions, there aren’t specific symptoms directly caused by high CRP. However, general symptoms of inflammation may include:
- fever
- weakness
- loss of appetite
- chills
- muscle aches
Symptoms can depend on any underlying conditions an individual suffers from also.


FAQs
CRP stands for C-reactive protein, a substance made by your liver. Your body releases CRP into your blood as a natural response to inflammation. Inflammation happens when your body is fighting an infection, illness, or healing from an injury. It’s your body’s way of protecting itself and starting the healing process.
Sometimes, inflammation is short-term and helpful, but if it lasts too long, it can harm your body.
A CRP test measures the amount of this protein in your blood to check if there’s inflammation in your body. However, it doesn’t tell us the exact cause of the inflammation.
The CRP test is most often recommended if you have symptoms of an infection. These symptoms might include fever, chills, rapid breathing, muscle aches, or vomiting. You might also notice symptoms specific to the part of your body that’s affected, such as issues with your chest, urine, skin, or gut. These are the most common areas where infections occur.
The test can also be helpful if you suspect you have a chronic condition like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus.
Additionally, CRP levels can be used to monitor how well a condition is responding to treatment. If the treatment is working, CRP levels should go down over time.
A CRP test helps detect inflammation in your body. Inflammation is a natural response that helps you heal from injuries or infections. However, if inflammation lasts too long, it can cause problems.
Mild inflammation can be normal after small things like a cut or a mild viral infection. But high levels of inflammation might be a sign of something more serious, like a bacterial infection or a chronic autoimmune condition. Knowing about them allows for tests to be done and treatment offered.
A high CRP level can have many causes, most commonly infections or chronic diseases.
Infections:
- Viral infections: Conditions like the flu, COVID-19, the common cold, or infections in the liver or gut.
- Bacterial infections: These can occur anywhere in the body, including the chest, skin, gut, urinary tract, or in abscesses (pockets of infection).
- Other infections: Rare infections like fungal infections or parasitic illnesses such as malaria.
Chronic inflammatory conditions:
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Inflammation mainly in the joints.
- Lupus: An inflammatory disease affecting many parts of the body, including the lungs, skin, kidneys, and blood.
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Conditions like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, which mostly affect the bowel but can also impact the skin and joints.
- Vasculitis: Inflammation of blood vessels, which can affect different body parts, such as the skin, lungs, kidneys, brain, or nerves.
- Psoriatic arthritis: A type of arthritis that causes joint pain and swelling, often in people with the skin condition psoriasis.
- Ankylosing spondylitis: Inflammation that mainly affects the spine.
Other possible causes:
- Cancer
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas.
- Appendicitis: Inflammation of the appendix.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease: An infection of the female reproductive organs, such as ovaries and uterus. It is often caused by sexually transmitted diseases.
- Recent surgery: Though this increase is usually only small, larger increases might suggest infection.
- Trauma
- Obesity
- Allergic reactions
- Cigarette smoking
- Depression
- Insomnia
- Pregnancy
- Fever
- Weakness
- Loss of appetite
- Chills
- Muscle aches
Symptoms can depend on any underlying conditions an individual suffers from also.
Infections:
- Respiratory infections: Cough, shortness of breath, or chest pain.
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs): Pain or burning when urinating, frequent urination, or cloudy urine.
- Skin infections: Redness, swelling, warmth, or tenderness.
- Gut infections: Diarrhoea, blood in stool, abdominal pain, or cramping.
Autoimmune conditions:
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Stiff, swollen, or painful joints, especially in the morning.
- Lupus (SLE): Tiredness, joint pain, or a rash (such as a butterfly-shaped rash on the face).
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Abdominal pain, diarrhoea (sometimes with blood), or weight loss.
- Vasculitis: Pain, skin rashes, or organ-specific symptoms like kidney problems or vision changes.
Tissue injury or trauma:
- Pain and swelling at the site of injury.
Cancer:
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Persistent fatigue (tiredness).
- Swollen lymph nodes.
- Pain or unusual lumps.
Please note that this is not a comprehensive list of symptoms and, if you are concerned about any of these conditions or any of your symptoms, particularly if your CRP is high, you should consult a healthcare professional.
- Ask about your symptoms and medical history.
- Order more tests, like blood tests or scans.
- Provide treatment, such as antibiotics, if needed.
The next steps will depend on what they find, so it is important to seek medical attention if the test is positive.
- High fever
- Severe or worsening pain
- Chest pain/ tightness
- Confusion
- Difficulty breathing
- Persistent symptoms without a clear cause
- Unexplained bleeding
- Any other concerns about your health
Once the cause is identified, your doctor will recommend treatment specific to that condition. For example:
- Rest and supportive care for mild viral illnesses, like a cold or flu.
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections.
- Other medications to manage chronic conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Your individual result report:
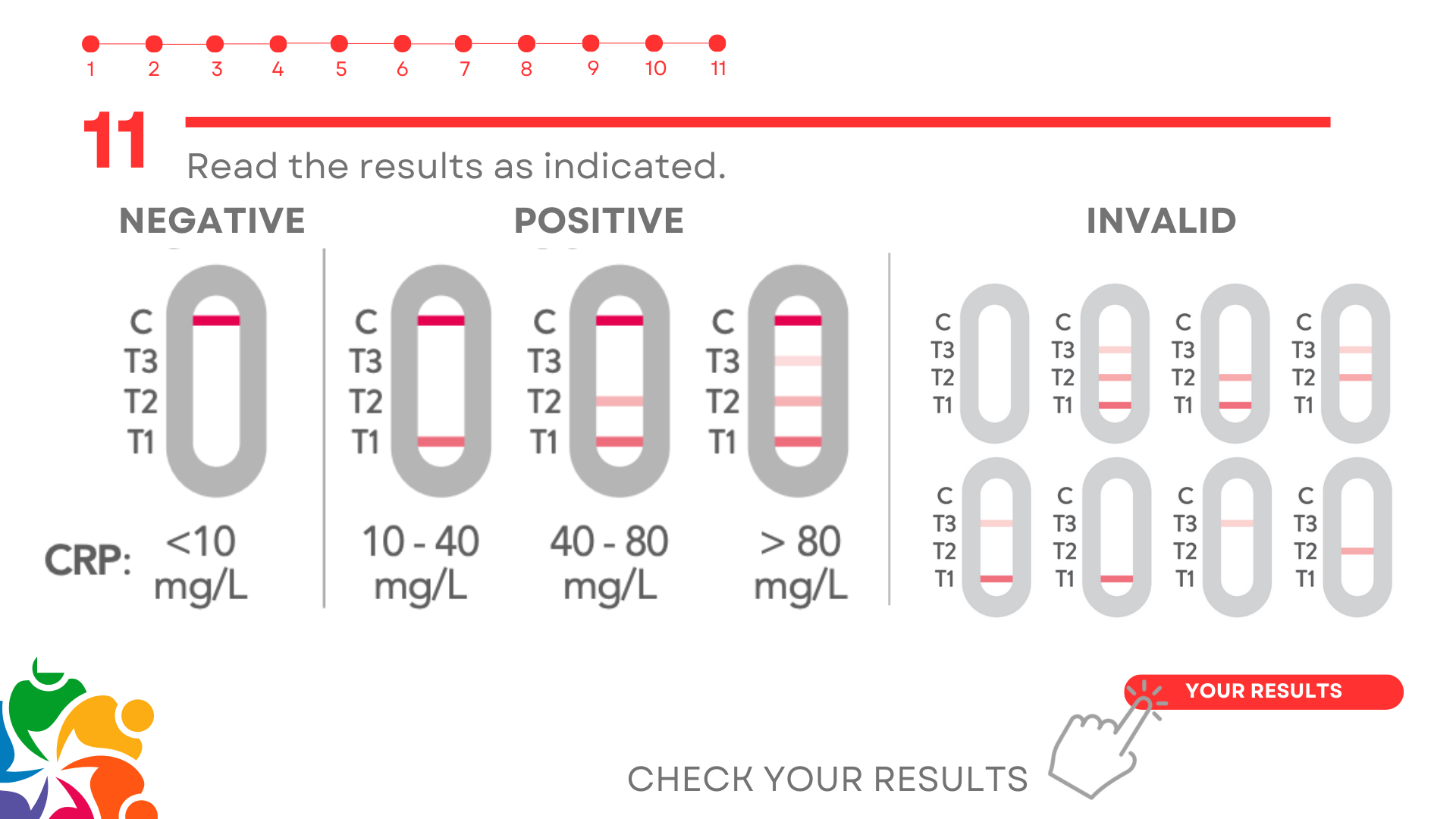
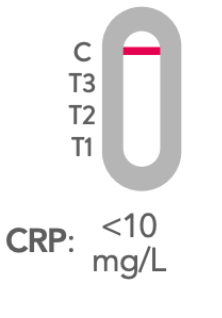
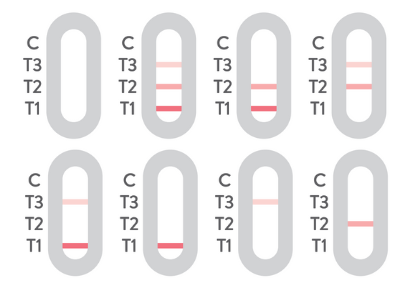
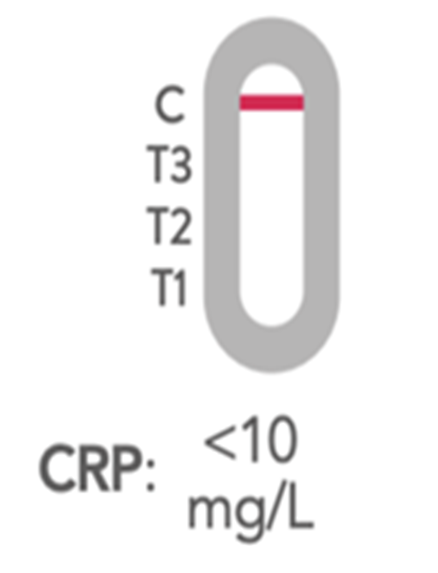
A negative result appears when a coloured band is visible along the C line (control) only, with no other lines showing.
This means your CRP level is less than 10 mg/L, which suggests there is no severe inflammation or infection in your body.
However, if your symptoms continue or worsen, you should consider repeating the test to check for changes or consult a doctor for further advice.

Your individual result report:
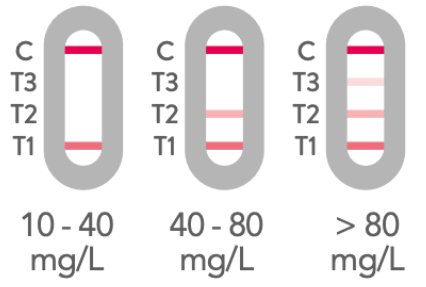
A positive result with a CRP level between 10 and 40 mg/L is indicated when there are lines visible at both C (control) and T1. This means your CRP is elevated. The lines may vary in brightness but this does not affect the result.
CRP levels in this range could have several causes, including:
- A viral infection, such as the flu or COVID-19
- The early stages of a bacterial infection
- General inflammation
A positive result with a CRP level between 40 and 80 mg/L is shown when lines are visible at C (control), T1, and T2. This indicates that your CRP is significantly raised. The lines may vary in brightness but this does not affect the result.
CRP levels in this range could have several causes, including:
- A viral infection, such as the flu or COVID-19
- A bacterial infection, such as pneumonia (lung) or gastroenteritis (gut). This is more likely at this level
- Inflammation from other underlying conditions
For more details on possible causes, please refer to the FAQ page. It’s essential to seek medical advice, as your doctor will need to perform further tests to identify the cause of this result and recommend appropriate treatment.
CRP levels over 80 mg/L can have several causes, including:
- A viral infection, such as the flu or COVID-19
- A bacterial infection, such as pneumonia (lung) or gastroenteritis (gut). This is more likely at this level
- Severe inflammation from other underlying conditions
For more details on possible causes, please refer to the FAQ page. It’s crucial to seek urgent medical advice, as your doctor will need to perform additional tests to determine the cause and provide appropriate treatment.
If there is no line at the ‘C’ band (Control), the test is invalid. You should disregard any result from that test strip.
This usually happens because of:
- An insufficient blood sample
- Incorrect sampling technique
If your result is invalid, repeat the test using a new test kit and a fresh blood sample. Be sure to carefully follow the instructions for accurate results.
Important Notes:
Results must be read exactly 5 minutes after completing the test procedure. Reading results earlier or later can lead to incorrect interpretation. You should consult a healthcare provider regardless of the result if symptoms or concerns persist.